This article describes Tricerat support for SQL Server ports, instances, and database aliases.
Note: The screenshots shown are from v6 but is applicable to v7 installs also.
Background
Tricerat customers sometimes ask about configuration flexibility for static ports, dynamic ports, named instances, and database server aliases.
This article describes configuration options available to our customers.
Tricerat Products Supported
Tricerat supports configuring static ports, dynamic ports, named instances, and database server aliases for:
- Simplify Suite
- Simplify Print Server
- Tricerat Service Based Printers
SQL Server Name Syntax
The syntax for specifying a SQL Server name is <host name or IP>``<, port number>``<\instance name>
<host name or IP>- This can be a machine name (resolvable by DNS) or an IP address.<, port number>- This can be a valid port number up to (and including) 65535.<\instance name>- This can be the name of an existing SQL Server instance
Static Ports
By default, Microsoft SQL Server listens for incoming client connections on TCP/IP port 1433.
Customers sometimes require SQL Server to listen on a different port by re-configuring SQL Server and internal firewalls.
To configure a static port when installing Tricerat products, use <host name or IP>``<, port number> syntax.
The following example configures a Simplify Suite installation to use SQL Server host TRICERAT-SQLDB and port number 11119:
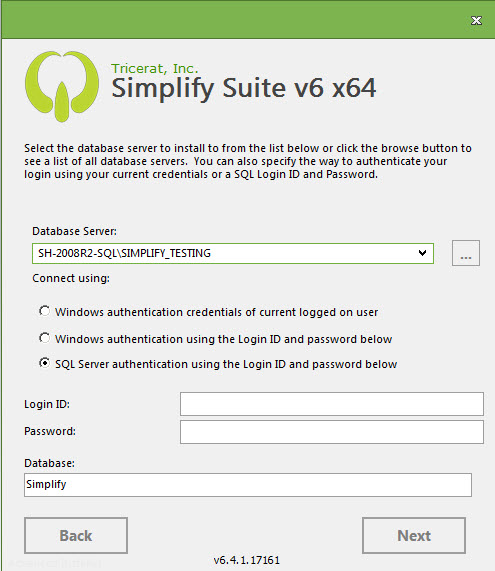 A named instance always corresponds to a specific port number. In this sense a unique port number is equivalent to a named instance.
A named instance always corresponds to a specific port number. In this sense a unique port number is equivalent to a named instance.
While possible, using a port number to configure a connection to a named instance of SQL Server is contrary to the intent of named instances and is not recommended.
Note: When both a port number and a named instance are provided, SQL Server ignores the instance name. Accordingly, when a port number and a named instance are provided to a Tricerat product installer, the port number is used and the instance name is discarded.
Database Server Aliases
SQL Server supports the concept of providing alias names for a database server. An alias is a combination of port and instance information that uniquely identifies a given SQL Server.
Customers configure database server aliases to provide operational flexibility to re-host databases without the need to revise client side configuration information.
The Microsoft SQL Server Browser is responsible for finding and resolving the actual server when a database server alias is used.
Tricerat products do not need to have any special knowledge of database server aliases for a given SQL Server.
Helpful Links
The following link describes how to configure SQL Server to listen on a port:
The following link describes how to manage database server aliases in SQL Server:
- Page: